原标题:有机酸和中链脂肪酸组合替代日粮中氧化锌对断奶仔猪生长,消化率和免疫力的影响
Effects of dietary combinations of organic acids and medium chain fatty acids as a replacement of zinc oxide on growth, digestibility and immunity of weaned pigs
作者:Y. Kuang 1, Y. Wang 1, Y. Zhang, Y. Song, X. Zhang, Y. Lin, L. Che, S. Xu, D. Wu, B. Xue∗, Z. Fang∗
Key Laboratory for Animal Disease Resistance Nutrition of the Ministry of Education, Animal Nutrition Institute, Sichuan Agricultural University, Ya’an 625014, China
来源:Animal Feed Science and Technology 208 (2015) 145–157
翻译:肠动力研究院 梁琦
【摘要】本研究通过两个实验来评估有机酸和中链脂肪酸(MCFA)的固态混合物作为氧化锌(ZnO)的替代品对断奶仔猪生长、消化率和免疫力的影响。实验1:对照组(CON)日粮中添加抗生素(分别含有纯的硫酸粘杆菌素和恩拉霉素,0.02g / kg日粮)和ZnO(2.5g/kg日粮),另一组日粮则不添加ZnO但在日粮中添加3g/kg的SF3(含甲酸钙,乳酸钙,柠檬酸和MCFA分别为340,160,70和130g/kg)。120头杂交仔猪(21日龄,6.36±0.80kg)预饲相同日粮1周。然后饲喂CON或SF3日粮4周(第2周不再向CON日粮中添加ZnO),每组6个重复(10个仔猪/栏)。试验表明,与对照组相比,SF3组在实验前两周的采食量更高(P <0.001),在第4周结束时仔猪体重显著提高(P<0.05),并且在实验第一周仔猪的料肉比显著降低(P <0.01)。
实验2:日粮同实验1一样,除了日粮以3g/kg的氧化铬替换同样剂量的玉米(评估日粮中氨基酸(AA)的表观回肠消化率(AID))。选取14只杂交仔猪(28日龄,9.05±1.38kg)分别圈养在代谢笼中,喂食CON日粮一周后,饲喂CON或SF3日粮两周,每种日粮喂食7头猪(4头母猪和3头公猪)。试验表明,与对照组相比,饲喂SF3的仔猪的大部分氨基酸的回肠表观消化率显著提高(P <0.05),血浆肿瘤坏死因子α(TNF-α)显著降低(P <0.05),但血浆中IgG浓度显著提高(P<0.05),回肠和直肠乳酸菌含量增加(P <0.05),空肠AA转运蛋白增多(P <0.05)和调节细胞因子的表达水平上升(TGF-β),但空肠促炎细胞因子的表达量下降(TNF-α)(P<0.05)。
研究结果表明:在实际生产条件下,与ZnO相比,在断奶仔猪日粮中添加有机酸和MCFA的混合物更有利于仔猪的生长。仔猪生长性能的提高与AA消化率和免疫力的增强有关。刺激调节细胞因子的表达和下调促炎细胞因子的表达水平可能随着有机酸的消耗而增加乳酸菌繁殖。
【关键词】有机酸;生长性能;肠道细菌繁殖;免疫力;断奶仔猪
以下是实验中相关图表
表1:实验前两周的日粮组成和成分(以饲喂为基础)
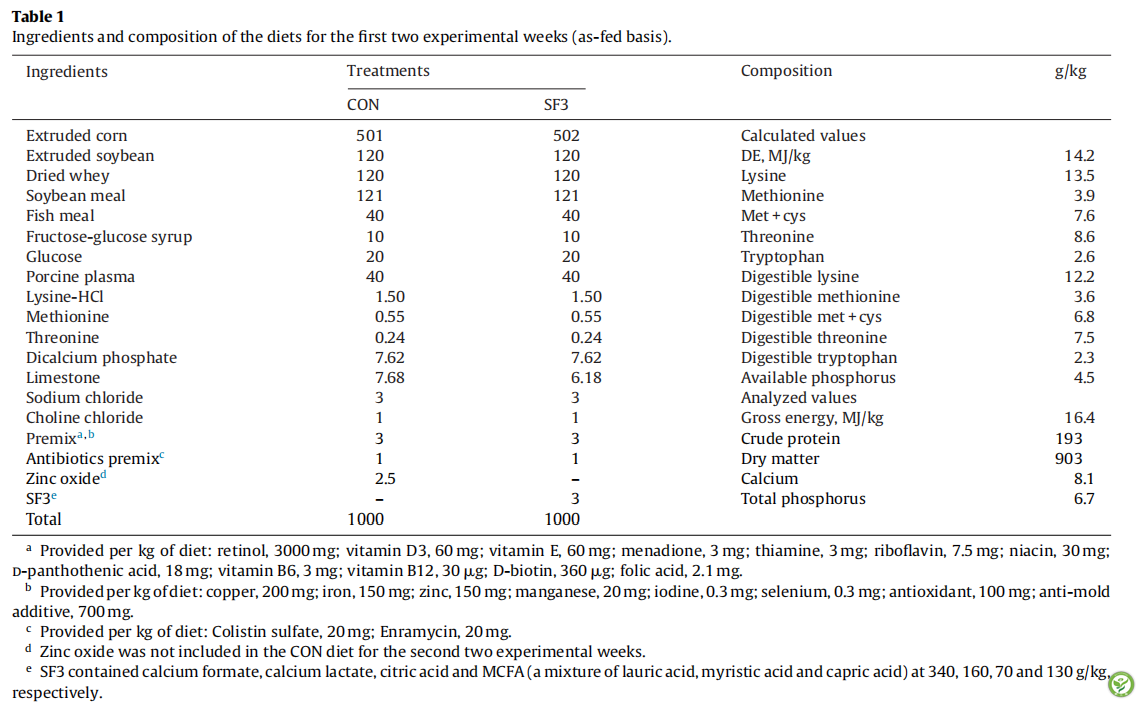
图1:饲喂CON或SF3日粮的仔猪(28日龄断奶)的空肠中肽和氨基酸转运基因PepT1,CAT2,EAAT3,b0,+ AT和y + LAT2的表达。数据为平均值±SEM,*, ***表示处理组之间的均值差异显著(P < 0.05 (*))和极显著(P < 0.001 (***))

表2:评估基因的编号,引物和产物大小

表3:本研究中使用的引物用于群特异性定量PCR。

表4:处理组日粮对21日龄断奶仔猪生长性能的影响
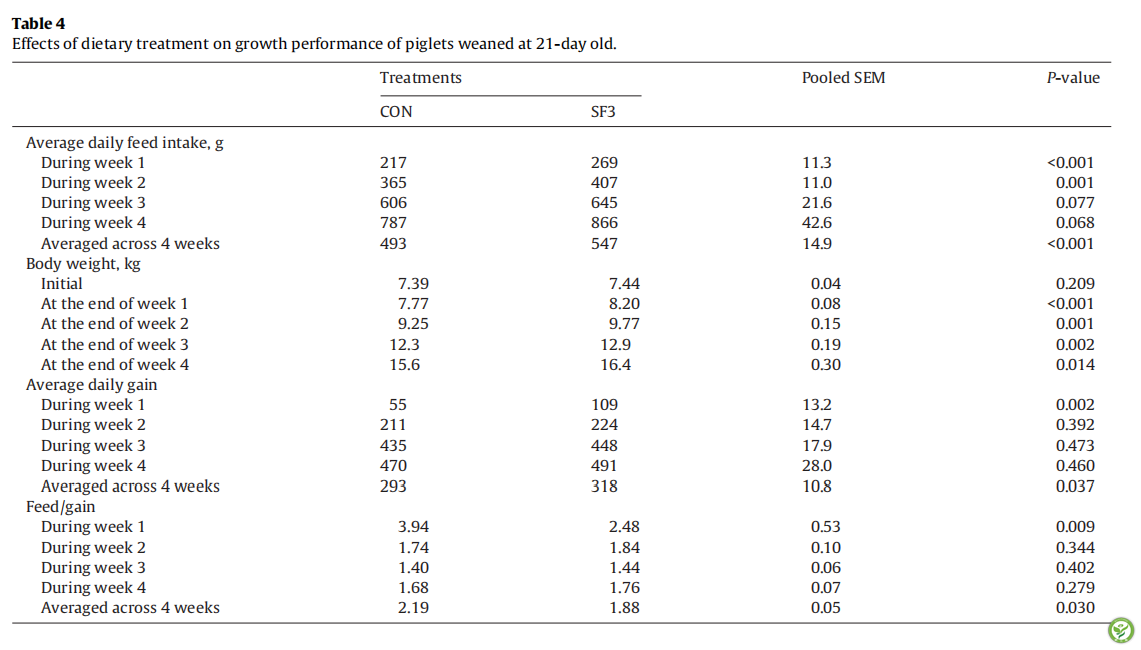
表5:处理组日粮对28日龄断奶仔猪生长性能的影响

表6:处理组日粮对28日龄断奶仔猪食物中氨基酸的表观回肠消化率的影响

图2:喂食CON或SF3饮食仔猪(28日龄断奶)回肠(A)和直肠(B)细菌含量(拷贝数/ g)。数据为平均值±SEM,*, **表示处理组之间的均值差异显著(P < 0.05 (*))和极显著(P < 0.01 (**))

图3:饲喂CON(A1-A3)或SF3(B1-B3))日粮的仔猪(28日龄断奶)的回肠食糜微生物群的聚合酶链反应(PCR)的16S rRNA靶向基因变性梯度凝胶电泳(DGGE)产物
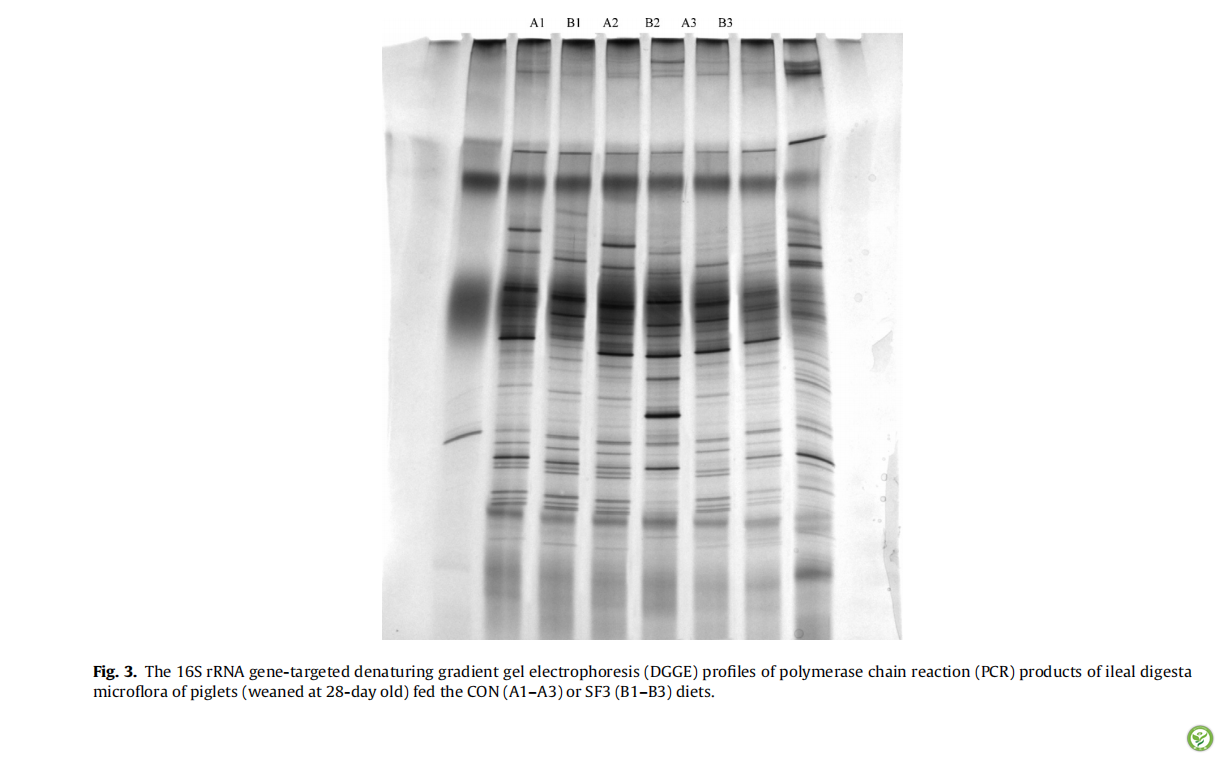
图4:饲喂CON(a1-a3)或SF3(b1-b3))日粮的仔猪(28日龄断奶)的直肠食糜微生物群的聚合酶链反应(PCR)的16S rRNA靶向基因变性梯度凝胶电泳(DGGE)产物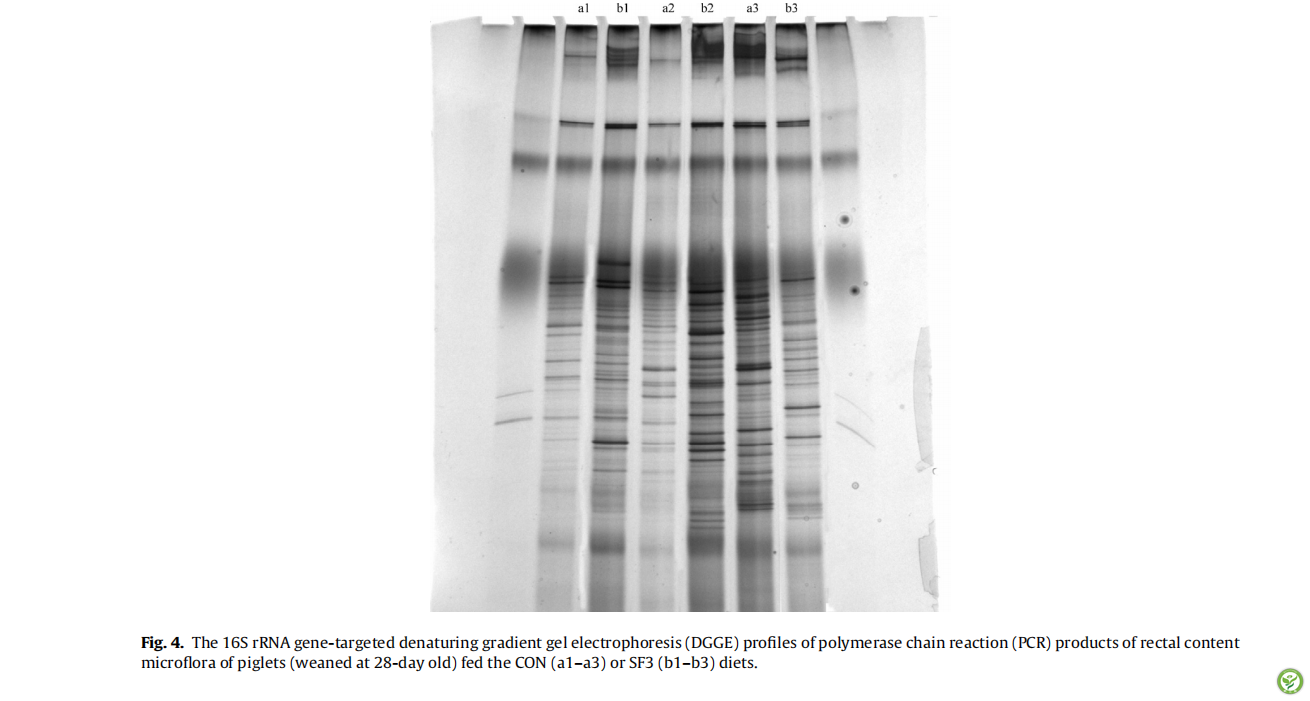 图5:饲喂CON或SF3日粮的仔猪(28日龄断奶)的回肠消化物和直肠内容物的微生物群的聚合酶链反应(PCR)的16S rRNA靶向基因变性梯度凝胶电泳(DGGE)的扩增带数量。数据为平均值±SEM,*, #表示处理组之间的均值差异显著(P < 0.05 (*))和差异显著(P < 0.1 (#))
图5:饲喂CON或SF3日粮的仔猪(28日龄断奶)的回肠消化物和直肠内容物的微生物群的聚合酶链反应(PCR)的16S rRNA靶向基因变性梯度凝胶电泳(DGGE)的扩增带数量。数据为平均值±SEM,*, #表示处理组之间的均值差异显著(P < 0.05 (*))和差异显著(P < 0.1 (#))
 图6:喂食CON(A1-A3)或SF3(B1-B3)日粮的仔猪(28日龄断奶)的回肠消化物中获得的变性梯度凝胶电泳(DGGE)图谱的相似性指数。
图6:喂食CON(A1-A3)或SF3(B1-B3)日粮的仔猪(28日龄断奶)的回肠消化物中获得的变性梯度凝胶电泳(DGGE)图谱的相似性指数。
图7:喂食CON(A1-A3)或SF3(B1-B3)日粮的仔猪(28日龄断奶)的直肠内容物中获得的变性梯度凝胶电泳(DGGE)图谱的相似性指数。
图8:饲喂CON或SF3日粮的仔猪(28日龄断奶)血浆中干扰素(IFN)-γ,肿瘤坏死因子(TNF)-α,白细胞介素(IL)-10和免疫球蛋白(Ig)-G的浓度。数据为平均值±SEM。*表示处理组之间的均值差异显著(P < 0.05)

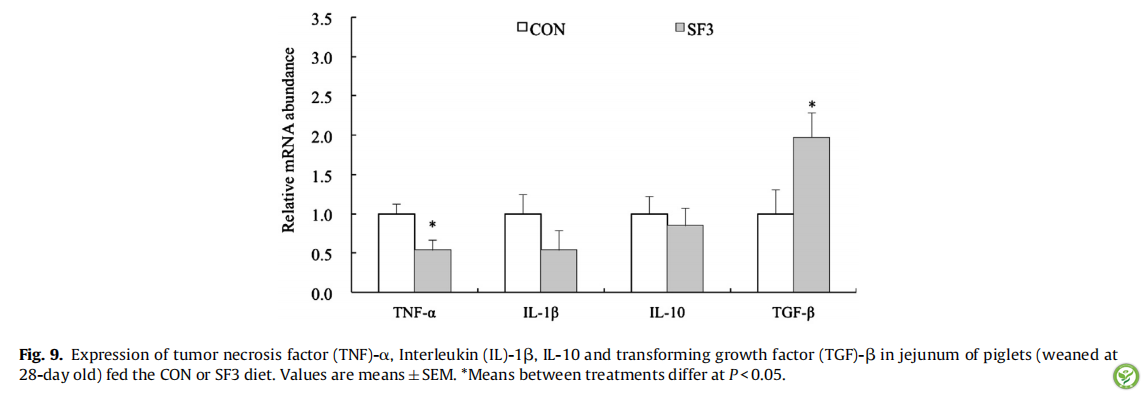
图9:饲喂CON或SF3日粮的仔猪(28日龄断奶)空肠中肿瘤坏死因子(TNF)-α ,白细胞介素(IL)-1β,IL-10和转化生长因子(TGF)-β的表达水平。数据为平均值±SEM。*表示处理组之间的均值差异显著(P < 0.05)
启示
实际生产条件下,与ZnO相比在断奶仔猪日粮中添加SCFA和MCFA的更有利于仔猪生长。断奶仔猪生长性能的提高与氨基酸消化率和免疫力的增强有关。刺激调节细胞因子的表达和下调促炎细胞因子的表达水平的可能随着有机酸的消耗而增加乳酸菌繁殖。
Abstract
Two experiments were conducted to evaluate effects of dietary solid mixture of organic acids and medium chain fatty acids (MCFA) as a replacement of zinc oxide (ZnO) on growth, digestibility and immunity of weanling pigs. In Exp. 1, the diet with supplemental antibiotics (containing pure Colistin sulfate and Enramycin, respectively, at 0.02 g/kg diet) and ZnO (2.5 g/kg diet) was used as the control (CON) group, and another diet without supplemental ZnO was prepared by inclusion of the SF3 (containing calcium formate, calcium lactate, citric acid and MCFA at 340, 160, 70 and 130 g/kg, respectively) at 3 g/kg diet. A total of 120 crossbred piglets (21-day old, 6.36 ± 0.80 kg) were fed the same commercial prestart diet for one week and then fed the CON or SF3 diet for four weeks (ZnO was no longer supplemented in the CON diet during the second two-weeks), with 6 replicate pens (10 piglets/pen) per diet. Compared with the CON-fed piglets, the SF3-fed piglets had higher (P<0.001) feed intake during the first two experimental weeks, higher (P<0.05) body weight at the end of each of the four experimental weeks, and lower (P < 0.01) ratio of feed to gain during the first experimental week. In Exp. 2, diets were the same as in Exp. 1, except that chromium oxide was included at 3 g/kg diet at the expense of corn to evaluate apparent ileal digestibility (AID) of dietary amino acids (AA). Fourteen crossbred piglets (28-day old, 9.05 ± 1.38 kg) were housed individually in metabolism cages, fed the CON diet for one week and then fed the CON or SF3 diet for two weeks with 7 pigs (4 female and 3 male) per diet. Compared with the CON-fed piglets, the SF3-fed piglets had higher (P<0.05) AID of a majority of AA, lower (P<0.05) plasma tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) but higher (P<0.05) plasma immunoglobulin-G concentrations, more (P<0.05) ileal and rectal Lactobacillus content, and upregulated (P<0.05) jejunal AA transporters (EAAT3 and CAT2) and regulatory cytokine (transforming growth factor beta) expression but downregulated (P<0.05) jejunal proinflammatory cytokine (TNF-α) expression. Taken together, dietary supplementation with a mixture of organic acids and MCFA contributed more than ZnO to growth of weanling pigs under commercial conditions. The improved growth of pigs was associated with increased AA digestibility and immunity. The stimulated regulatory cytokine expression and downregulated proinflammatory cytokine expression might be associated with increased proliferation of Lactobacillus following organic acids consumption.
Conclusion
Dietary supplementation with short- andmedium-chain fatty acids contributedmore than ZnO to growth of weanling pigs under commercial conditions. The improved growth of pigs was associated with increasedAAdigestibility and immunity. The stimulated regulatory cytokine expression and downregulated proinflammatory cytokine expression might be associated with increased proliferation of Lactobacillus following organic acids consumption
如您需原文,请联系本文作者和出版方,或请垂询肠动力研究院。本网站发布的所有资料将尽最大可能注明出处、作者及日期,如无意中侵犯了您的知识产权,请来信及时告知,我们将立即予以删除。
All information released by the WeChat Official Account will do its best to indicate the source, author and date. If we inadvertently infringe on your intellectual property, please inform us in time and we will delete it immediately.














