原标题:代谢组学特征揭示与母猪泌乳性能相关的潜在因素
Metabolomic Profiles Reveal Potential Factors that Correlate with Lactation Performance in Sow Milk
作者:ChengquanTan1, ZhenyaZhai 1, Xiaojun Ni1, HaoWang1, Yongcheng Ji
1, TianyueTang1, Wenkai Ren1,2, Hongrong Long1, Baichuan Deng1, Jinping Deng1
& YulongYin1,3
1 Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Animal Nutrition Control, Institute of Subtropical Animal Nutrition and Feed, College of Animal Science, South China Agricultural University, Guangzhou, 510642, P.R. China.
2 Jiangsu CoInnovation Center for Important Animal Infectious Diseases and Zoonoses, Joint International Research Laboratory of Agriculture and Agri-Product Safety of Ministry of Education of China, College of Veterinary Medicine, Yangzhou University, Yangzhou, 225009, China.
3 National Engineering Laboratory for Pollution Control and Waste Utilization in Livestock and Poultry Production, Institute of Subtropical Agriculture, The Chinese Academy of Sciences, Changsha, 410125, P.R. China.
来源:SCIENTIfIC REPOrTs | (2018) 8:10712 | DOI:10.1038/s41598-018-28793-0
翻译:肠动力研究院 梁琦
【摘要】母猪奶水中含有仔猪必需的营养素,然而迄今为止,奶水中代谢物水平与泌乳性能之间的关系尚未得到充分阐明。本文旨在利用代谢组学分析高泌乳(HL)或低泌乳(LL)性能的约克夏母猪(4.0±1.2胎次)奶水中代谢物的特征,试验分组是根据整个哺乳期(D1-D21)仔猪的增重进行分配,体重增加较高的断奶仔猪(4.38±0.64 kg)被定义为高泌乳性能组(HL),体重增加较低的断奶仔猪(3.24±0.79 kg)被定义为低泌乳性能组(LL),每组15头。分娩开始后4小时内收集初乳,在分娩后第18天收集成熟的奶水样品,利用GC-MS和LC-MS两种技术对HL组和LL组母猪奶水中代谢物和代谢途径展开分析。结果显示,在初乳中,HL组的乳脂浓度趋于升高(P = 0.05);与LL组比较,HL组甘露醇的水平显著降低(P <0.05),而葡萄糖醛酸内酯的水平显著升高(P <0.05)。在成熟奶水中,HL组的乳糖、肌酸、谷氨酰胺、谷氨酸、4-羟脯氨酸、丙氨酸、天冬酰胺和甘氨酸的水平显著高于LL组(P <0.05)。初乳和成熟奶水中两组脂肪酸的水平均无显著差异。研究表明,泌乳性能可能与母猪奶水中乳糖和几种氨基酸的含量有关,这些结果可用于开发新的饲料添加剂以改善母猪的泌乳性能。
以下为相关图表
表1:母猪初乳和成熟乳中脂肪,蛋白质,乳糖和总固体的浓度。SEM:平均标准误,每组n=15,LL:低泌乳力组,HL:高泌乳力组。
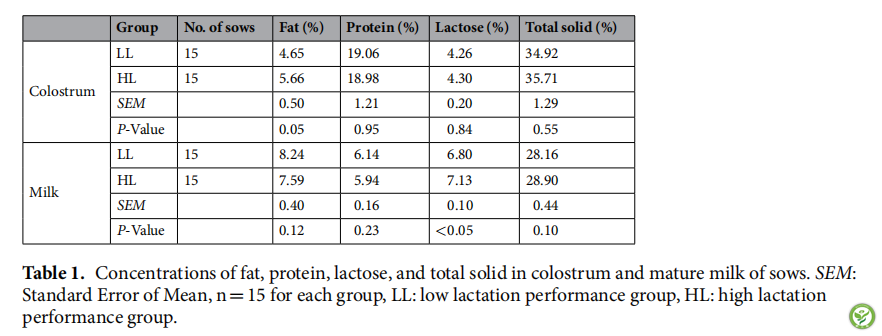
表2:与母猪泌乳性能有关的代谢物和代谢途径。
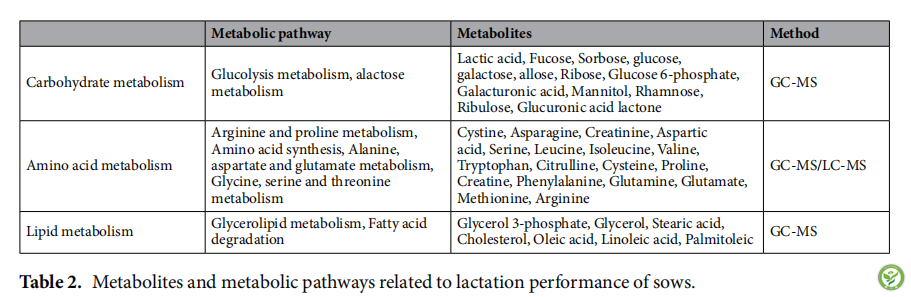
图1:通过使用LC-MS(A)或GC-MS(B)从初乳和成熟乳中获得的数据建立PCA模型的得分图。QC:质量控制样品;MHL:HL组中的成熟乳样品;MLL:LL组中的成熟乳样品;CHL:HL组初乳样品;CLL:LL组的初乳样品。
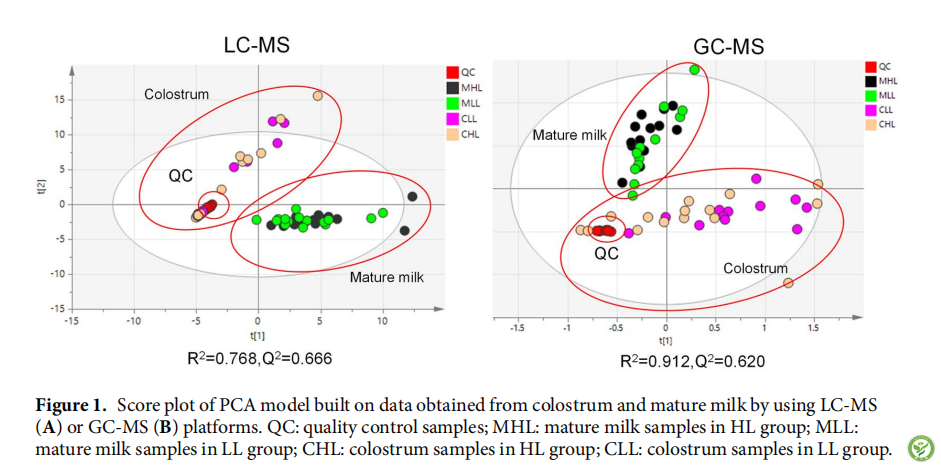
图2:初乳和成熟乳中氨基酸,碳水化合物和脂质代谢的PLS-DA模型得分图。 HL和LL组分别以蓝色或鲜绿色显示。
表3:初乳和成熟乳中HL和LL组之间的差异代谢产物。HL:高泌乳能力组目标代谢物/内标物的Te峰面积;LL:低泌乳性能下目标代谢物的Te峰面积;P值:t检验的Te P值;FC:倍数变化,HL组的峰面积/ LL组的峰面积。如果FC> 1,则说明HL组的代谢物浓度高于LL组,反之亦然。VIP:通过PLS-DA分析计算得出的可变重要性(VIP)值。
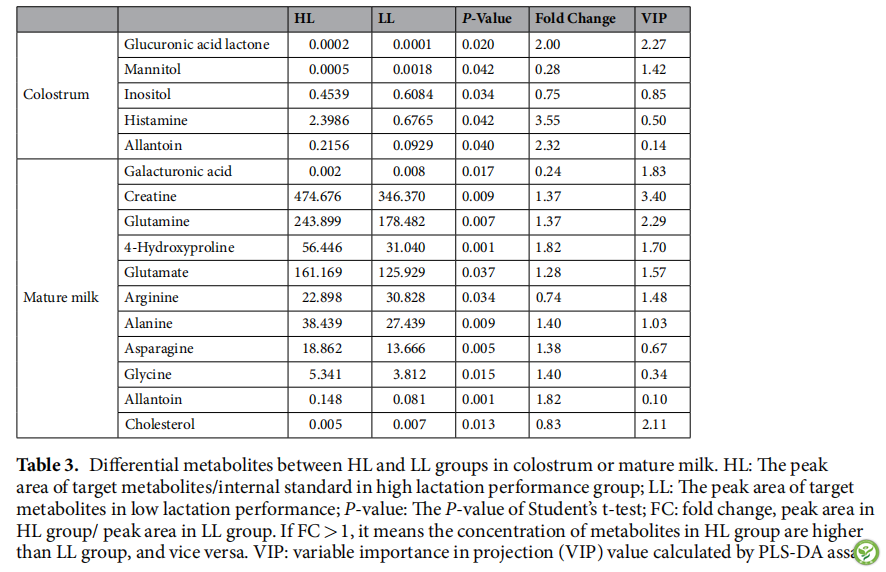
图3:母猪成熟乳中的氨基酸和衍生物发生变化。GC-MS / LC-MS平台检测到绿色标记的绿色代谢产物。不同的代谢物用箭头显示。
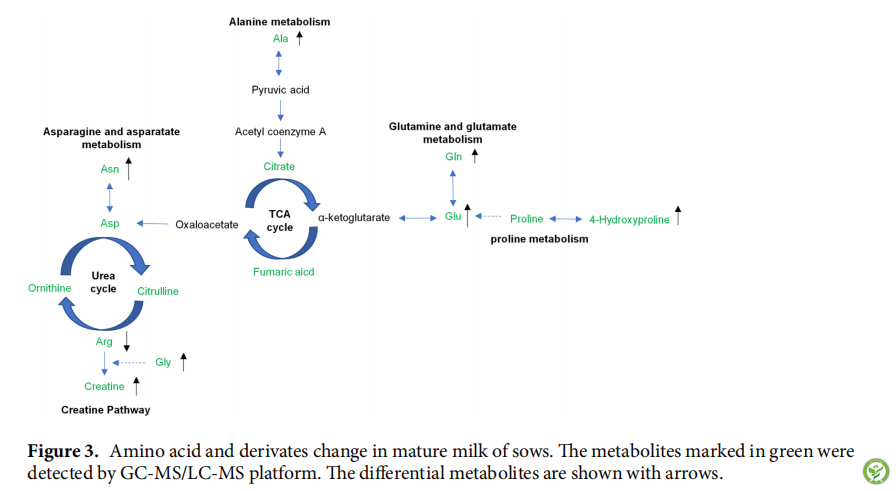
表4:HL和LL组母猪的泌乳性能。HL:高泌乳力组;LL:低泌乳力组;仔猪增重=断奶时的平均体重-出生后的平均体重。
表5:用于LC-MS分析的梯度程序。
总结
本文使用GC-MS和LC-MS技术,观察到泌乳性能高或低的母猪初乳和成熟乳中的代谢物及代谢途径之间存在显著差异。在这些代谢途径中,氨基酸代谢和碳水化合物代谢与母猪泌乳性能具有高相关性,而脂质代谢显示低相关性。含量升高的谷氨酰胺、谷氨酸,丙氨酸和天冬酰胺是与母猪高泌乳性能相关的关键代谢产物。这种特性可能归因于这些氨基酸对仔猪健康,肌肉发育和仔猪能量状况的益处。较高浓度的乳糖也是与高泌乳性能有关的关键因素,这表明能量供应对于泌乳性能也很重要。此外,初乳中甘露醇水平的升高和葡萄糖醛酸内酯水平的降低与泌乳性能低下有关。本文可以帮助研究人员了解提高母猪泌乳性能的关键因素,并为动物营养提供有益的信息。
Abstract
Sow milk contains necessary nutrients for piglets; however, the relationship between the levels of metabolites in sow milk and lactation performance has not been thoroughly elucidated to date. In this study, we analysed the metabolites in sow milk from Yorkshire sows with high lactation (HL) or low lactation (LL) performance; these categories were assigned based on the weight gain of piglets during the entire lactation period (D1 to D21). The concentration of milk fat in the colostrum tended to be higher in the HL group (P=0.05), the level of mannitol was signifcantly lower in the HL group (P<0.05) and the level of glucuronic acid lactone was signifcantly higher in the HL group (P<0.05) compared to those in LL group. In mature milk, the levels of lactose, creatine, glutamine, glutamate, 4-hydroxyproline, alanine, asparagine, and glycine were signifcantly higher (P<0.05) in the HL group than those in LL group. The level of fatty acids showed no signifcant diference between the two groups in both the colostrum and mature milk. This study suggested that lactation performance may be associated with the levels of lactose and several amino acids in sow milk, and these results can be used to develop new feed additives to improve lactation performance in sows.
Conclution
Using GC-MS and LC-MS techniques, signifcant diferences between the metabolites and metabolic pathways in the colostrum and mature milk of sows with high or low lactation performance were observed. Among these metabolic pathways, amino acid metabolism and carbohydrate metabolism are highly correlated with lactation performance of sows, while lipid metabolism shows weak correlation. Up-regulated glutamine, glutamate, alanine, and asparagine are the key metabolites correlated with high lactation performance. Tis property may be attributed to the benefts of these amino acids for intestinal health, muscle development, and energy status of piglets. Te higher concentration of lactose is also a key factor related to high lactation performance, which suggests that energy supply is also important for lactation performance. Besides, increased level of mannitol and lowered level of glucuronic acid lactone in the colostrum are related to low lactation performance. Tis study may help researchers to understand the key factors in improving the lactation performance and provide useful information for animal nutrition.
如您需原文,请联系本文作者和出版方,或请垂询肠动力研究院。本网站发布的所有资料将尽最大可能注明出处、作者及日期,如无意中侵犯了您的知识产权,请来信及时告知,我们将立即予以删除。
All information released by the WeChat Official Account will do its best to indicate the source, author and date. If we inadvertently infringe on your intellectual property, please inform us in time and we will delete it immediately.







