三丁酸甘油酯对LPS诱导的应激在肉鸡肠道能量状态、抗氧化能力及免疫应答的影响
Effects of Tributyrin on Intestinal Energy Status, Antioxidative Capacity and Immune Response to Lipopolysaccharide Challenge in Broilers
作者:Jiaolong Li1,Yongqing Hou1, Dan Yi1,Jun Zhang1,Lei Wang1,Hongyi Qiu1,Binying Ding1,2,*,and Joshua Gong3
1 Hubei Collaborative Innovation Center for Animal Nutrition and Feed Safety,
Hubei Key Laboratory of Animal Nutrition and Feed Science, Wuhan Polytechnic University, Wuhan 430023, China
来源:Asian Australas. J. Anim. Sci.
Vol. 28, No. 12 : 1784-1793 December 2015
http://dx.doi.org/10.5713/ajas.15.0286
【摘要】本试验旨在研究三丁酸甘油酯(TB)对脂多糖(LPS)诱导的应激在肉鸡生长性能、促炎细胞因子、肠道形态、能量状态、二糖酶活性和抗氧化能力的方面的影响。160羽Cobb肉鸡(1日龄,45.1±0.5 g)被随机分成2×2因子处理组,试验分组如下,1)对照组:饲喂基础日粮+腹腔注射等量的无菌盐水;2)TB组:饲喂添加500mg/kgTB的基础日粮+腹腔注射等量的无菌盐水;3)LPS组:饲喂基础日粮+腹腔注射500µg/kg(BW)LPS;4)TB+LPS组:饲喂添加500mg/kgTB的基础日粮+腹腔注射500µg/kg(BW)LPS。每组4羽,每组10个重复,实验为期26天。每周记录肉鸡体重和采食量;其中无菌盐水和LPS分别于试验的第22,24和26天对肉鸡进行腹腔注射;第27天,在注射LPS或生理盐水后24h,处死所有肉鸡并收集肠道样品。结果显示,与对照组相比,日粮添加TB对肉鸡生产性能(平均日采食量和平均日增重)无显著影响,但在试验第22-26天相比于对照组,LPS组肉鸡的平均日增重显著降低(P <0.05)。日粮添加TB能够抑制LPS诱导的肉鸡IL-1β(空肠和回肠)、IL-6(十二指肠和空肠)、PGE2(十二指肠),以及TNOS(回肠)和iNOS(空肠)表达水平的上升;此外,研究还发现,日粮添加TB能够缓解LPS诱导的肉鸡回肠中ATP、ADP、TAN以及空肠中CAT水平的降低。综上,研究结果表明,日粮添加TB能够减少LPS诱导的肉鸡小肠中促炎细胞因子的表达以及提高肠道能量状态,抗氧化能力。
【关键词】三丁酸甘油酯;脂多糖;肠道免疫应答;肉鸡
以下是试验相关图表
表1:基础日粮的组成及营养水平
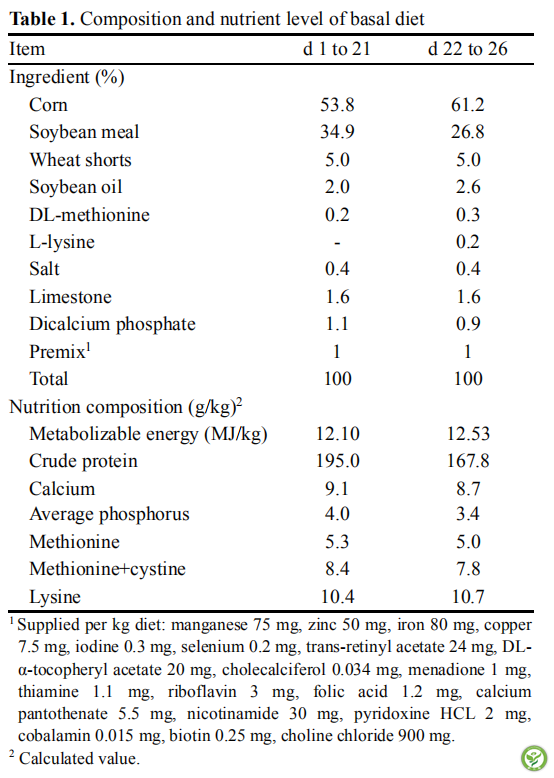
图1:用于诱导肉鸡免疫应激的脂多糖(LPS)剂量的初步研究。将24羽Cobb肉鸡(雄性,22日龄)随机分成4组(对照组,0.25mg / kg体重[BW] LPS,0.5mg / kg BW LPS和1mg / kg BW LPS)。在22日龄时,0.25 mg / kg BW LPS,0.5 mg / kg BW LPS和1 mg / kg BW LPS组的肉鸡腹腔注射LPS,剂量分别为0.25,0.5和1 mg / kg BW,对照组则腹腔注射剂量为0.25mg / kg BW的无菌盐水。LPS或盐水注射后24h从肉鸡翼静脉中穿刺采血测定IL-1β的水平。并在22-28日龄,记录肉鸡的平均日采食量。数据=平均值±标准误(n=6)。a,b,c在IL-1β水平上具有不同上标的平均值显著不同(p <0.05)。A,B在平均日采食量(ADFI)具有不同上标的平均值显著不同(p <0.05)。

表2:日粮添加TB对LPS诱导的肉鸡肠道中促炎细胞因子表达水平的影响
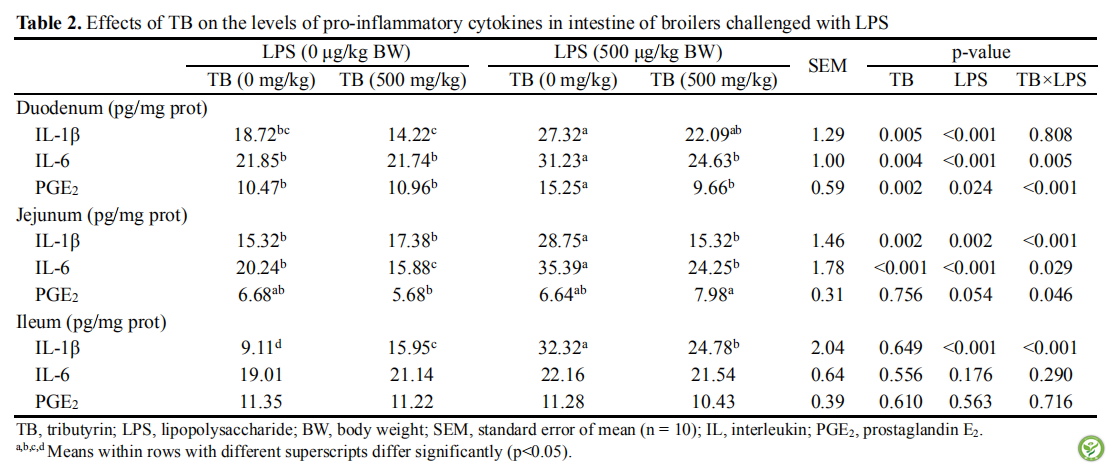
表3:日粮添加TB对LPS诱导的肉鸡肠道形态的影响
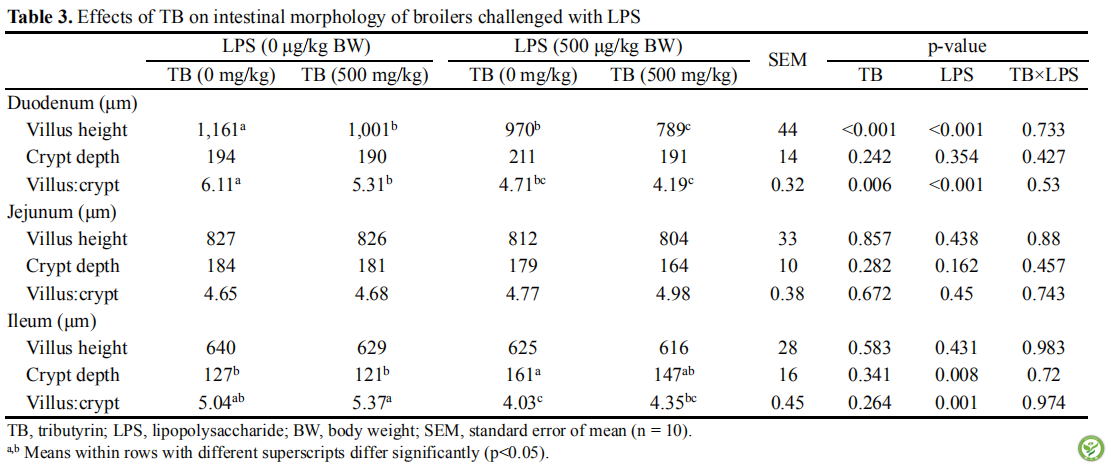
表4:日粮添加TB对LPS诱导的肉鸡肠道中二糖酶活性的影响
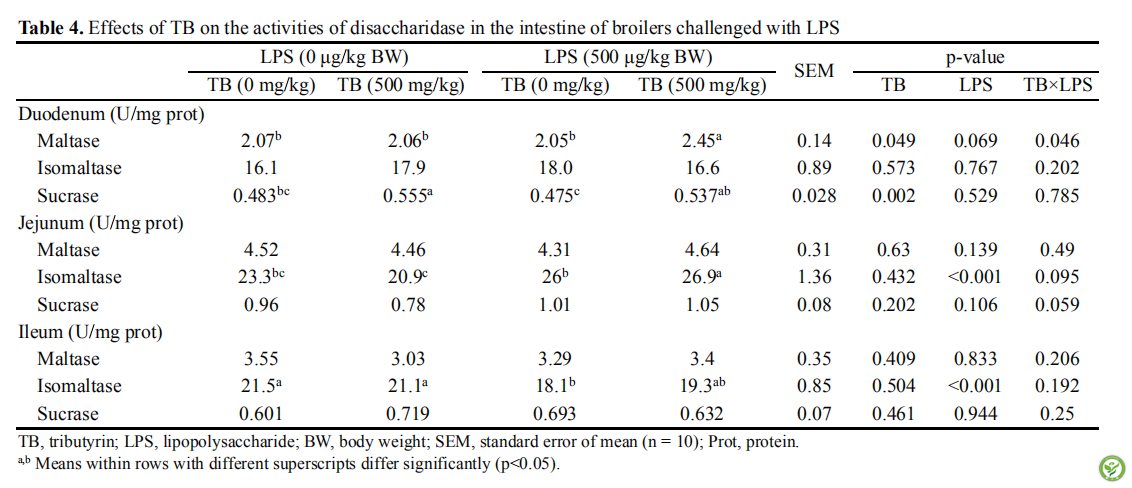
表5:日粮添加TB对LPS诱导的肉鸡小肠能量状态影响
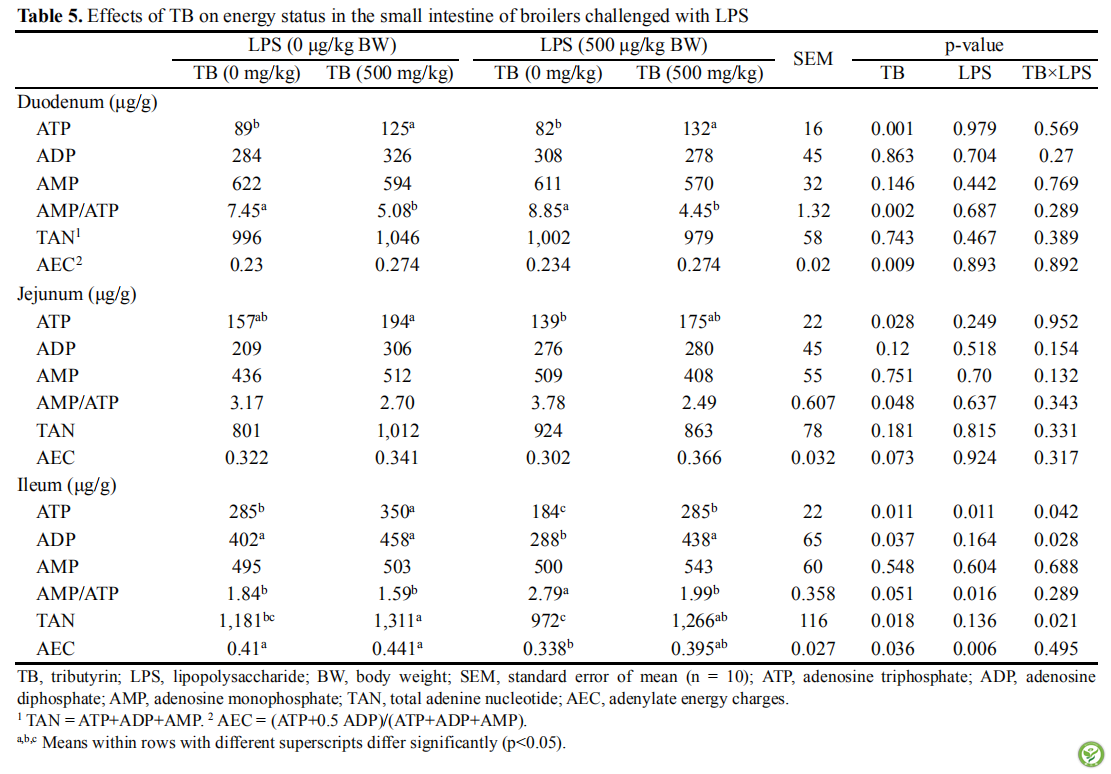
表6:日粮添加TB对LPS诱导的肉鸡肠道中氧化指标的影响

结论
总之,在LPS诱导的肉鸡日粮中添加500 mg/kg TB可抑制促炎细胞因子的释放,提高肠道能量状态,并增强肠道抗氧化能力。
Abstract
This study was carried out to investigate the effects of tributyrin (TB) on the growth performance, pro-inflammatory cytokines, intestinal morphology, energy status, disaccharidase activity, and antioxidative capacity of broilers challenged with lipopolysaccharide (LPS). A total of 160 one-day-old Cobb broilers were allocated to 1 of 4 treatments, with 4 replicated pens per treatment and 10 birds per pen. The experiment consisted of a 2×2 factorial arrangements of treatments with TB supplementation (0 or 500 mg/kg) and LPS challenge (0 or 500 μg/kg body weight [BW]). On days 22, 24, and 26 of the trial, broilers received an intraperitoneal administration of 500 µg/kg BW LPS or saline. Dietary TB showed no effect on growth performance. However, LPS challenge decreased the average daily gain of broilers from day 22 to day 26 of the trial. Dietary TB supplementation inhibited the increase of interleukin-1β (in the jejunum and ileum), interleukin-6 (in the duodenum and jejunum), and prostaglandin E2 (in the duodenum) of LPS-challenged broilers. Similar inhibitory effects of TB in the activities of total nitric oxide synthase (in the ileum) and inducible nitric oxide synthase (in the jejunum) were also observed in birds challenged with LPS. Additionally, TB supplementation mitigated the decrease of ileal adenosine triphosphate, adenosine diphosphate and total adenine nucleotide and the reduction of jejunal catalase activity induced by LPS. Taken together, these results suggest that the TB supplementation was able to reduce the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines and improve the energy status and anti-oxidative capacity in the small intestine of LPS-challenged broilers.
Key Words: Tributyrin, Lipopolysaccharide, Intestine, Immune Response, Broilers
Conclusion
In conclusion, dietary supplementation of 500 mg/kg TB inhibited the proinflammatory cytokines release, improved the intestinal energy status, and enhanced the intestinal anti-oxidative capacity in LPS-challenged broilers.
如您需原文,请联系本文作者和出版方,或请垂询肠动力研究院。本网站发布的所有资料将尽最大可能注明出处、作者及日期,如无意中侵犯了您的知识产权,请来信及时告知,我们将立即予以删除。
All information released by the WeChat Official Account will do its best to indicate the source, author and date. If we inadvertently infringe on your intellectual property, please inform us in time and we will delete it immediately.






