Oral tributyrin prevents endotoxin-induced lipid metabolism disorder
作者:Makoto Miyoshi a, Norihito Iizuka a, Shota Sakai a, Mayu Fujiwara a,MichikoAoyama-Ishikawa a, Noriaki Maeshige a, Yasuhiro Hamada b, Michiko Takahashi c,Makoto Usami a, c, *
a Division of Nutrition and Metabolism, Kobe University Graduate School of Health Sciences, Kobe 654-0142, Japan
b Department of Therapeutic Nutrition, Institute of Health Bioscience, The University of Tokushima Graduate School, Tokushima 770-8503, Japan
c Department of Nutrition, Kobe University Hospital, Kobe University School of Medicine, Kobe 650-0017, Japan
来源:Clinical Nutrition ESPEN 10 (2015) e83ee88,doi: 10.1016/j.clnesp.2015.02.001.
摘要:背景与目的:相关研究已表明(1)脓毒症可导致机体脂质和脂蛋白代谢紊乱(2)丁酸能够促进过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体(PPARs)表达水平的增加,已知PPARs是一种能诱导脂肪酸氧化和合成的关键核激素受体(3)口服三丁酸甘油酯(乳制品中可产生丁酸的前体物质)可通过增加肝细胞中丁酸水平来降低NF-kB的活性从而减轻脂多糖(LPS)诱导的肝损伤。本研究旨在阐明口服三丁酸甘油酯对LPS诱导的脂质代谢紊乱大鼠的保护机制。方法:76只Wistar大鼠(雄性,7-8周龄)随机分成2组,三丁酸甘油酯组:先口服1g/kg三丁酸甘油酯+1h后腹腔注射10mg/kg LPS(大肠杆菌O111:B4);载体组:脂质乳剂+生理盐水+1h后腹腔注射10mg/kg LPS(大肠杆菌O111:B4),试验期间大鼠自由饮水12h直至它们被处死。分别在LPS注射后的0,1.5,6和24 h处死部分大鼠,收集血液和肝组织展开分析。除了检测血浆中脂质水平外,试验还通过RT-PCR或WB方法分析了核激素受体(PPAR),脂肪酸代谢相关酶和乙酰H3蛋白在肝组织中的表达水平。结果:(1)大鼠腹腔注射LPS 24h后,三丁酸甘油酯能够减缓血浆中甘油三酯,总胆固醇(TC)和低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(LDL-C)水平的升高。(2)口服三丁酸甘油酯在基础水平上可增强肝脏中PPAR和组蛋白H3的表达。(3)三丁酸甘油酯能够减缓LPS对PPARs诱导的脂肪酸氧化相关酶如:脂肪酸转运蛋白(FATP)和脂肪酸结合蛋白(FABP)或脂肪酸合成相关的酶如固醇调节元件结合蛋白-1c(SREBP-1c)的抑制作用。结论:口服三丁酸甘油酯主要通过加快脂肪酸的氧化来防止内毒素血症的大鼠中血浆甘油三酯,TC和LDL-C水平的升高。
关键词:丁酸;脂多糖;脂质代谢紊乱;过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体;脂肪酸氧化
以下为相关图表
表1:用于实时-PCR的引物序列
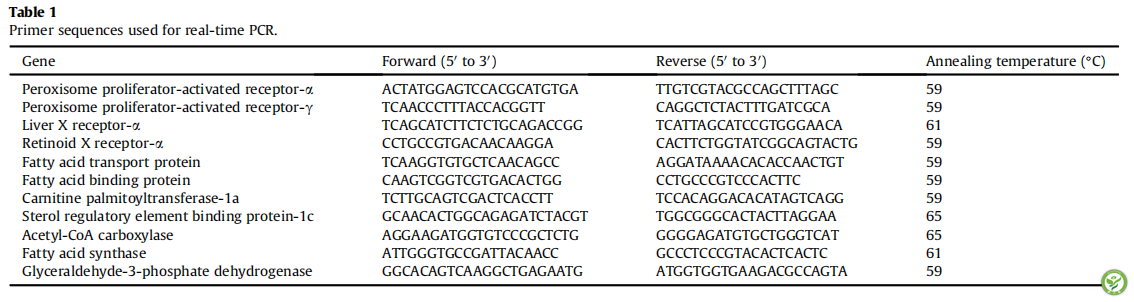
表2:LPS攻毒后0,24h内收集的血液生化指标
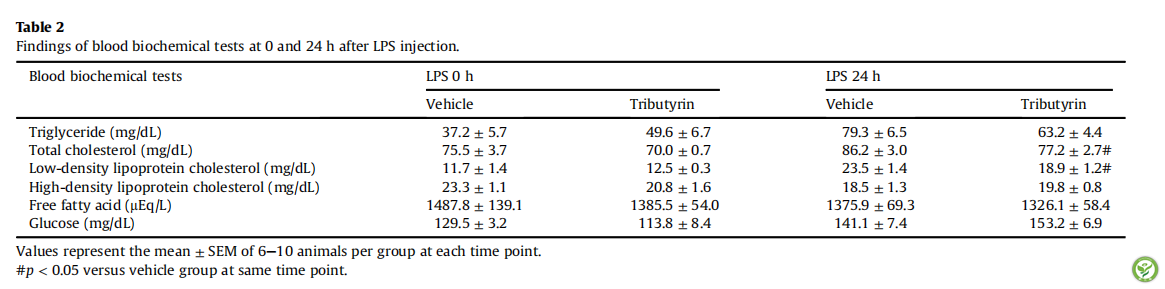
图1:在注射LPS 0,1.5,6h后三丁酸甘油酯对大鼠肝脏中核激素受体mRNA表达量的影响。(A)PPAR-α,(B)PPAR-γ,(C)LXR-α;数据=均值±标准误(通过每个时间点每组8-10只动物计算而得)。相同时间点,*P <0.05,**P <0.01相对于0h,#P <0.05,##P <0.01相对于载体组。
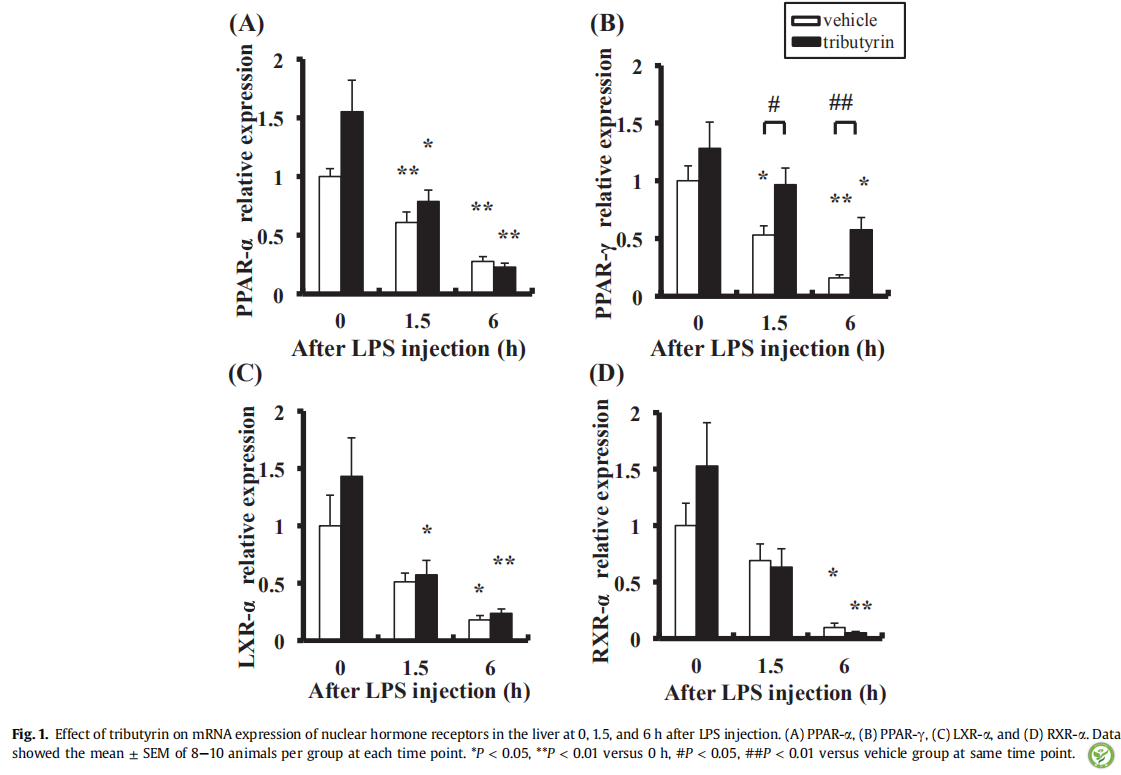
图2:LPS攻毒后0,6h大鼠肝脏中PPAR-α和PPAR-γ蛋白质的表达水平。特定条带(A)和光密度分析(B)和(C)。从每组4-6只小鼠中汇总获得的蛋白质样品。
图3:LPS攻毒后0,1.5,6h三丁酸甘油酯对大鼠肝脏中脂肪酸β-氧化酶的mRNA表达量的影响。(A)FATP,(B)FABP,和(C)CPT-1a。数据=均值±标准误(通过每个时间点每组8-10只动物计算而得)。在相应时间点,**P <0.01相对于0h,##P <0.01相对于载体组。
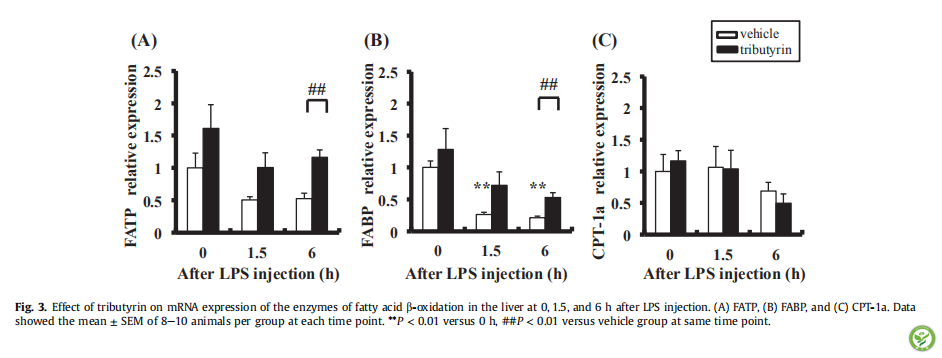
图4:LPS攻毒后0,1.5,6h三丁酸甘油酯对大鼠肝脏中脂肪酸合成酶的mRNA表达量的影响。(A)SREBP-1c,(B)ACC,和(C)FAS。数据表示均值±标准误(通过每个时间点每组8-10只动物计算而得)。在相同时间点,*P <0.05,**P <0.01相对于0h,#P <0.05,相对于载体组。
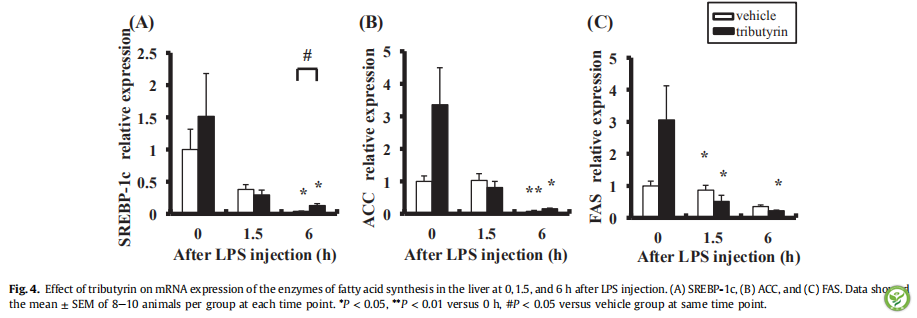
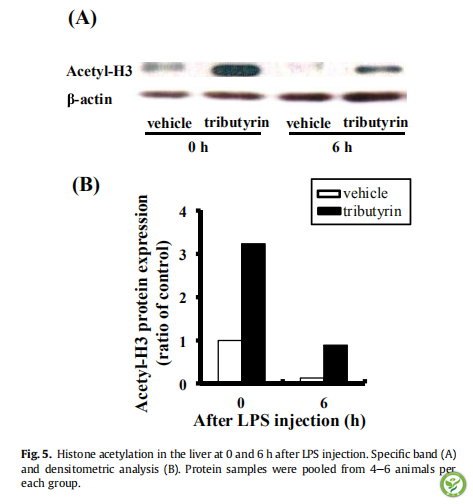
图5:LPS攻毒后0,6h大鼠肝脏中组蛋白乙酰化的水平,特定条带(A)和光密度分析(B)和(C)。从每组4-6只小鼠中汇总获得的蛋白质样品。
Conclusion
总之,本研究表明,三丁酸甘油酯通过加快肝脏中脂肪酸的氧化来防止LPS诱导的血浆中TG,TC和LDL-C水平的升高。口服三丁酸甘油酯可能是一种在急性炎症如脓毒症期间治疗脂质代谢紊乱的新方法。
Abstract
Background & aims: Sepsis leads to dysregulation of lipid and lipoprotein metabolism. Butyrate increases peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs), which are key nuclear hormone receptors to induce fatty acid oxidation and synthesis. Oral administration of tributyrin, a prodrug of butyrate contained in dairy products, suppresses lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced liver injury through attenuating nuclear
factor-kB activity with an increased hepatoportal butyrate level. In this study, we elucidated the protective effect of oral administration of tributyrin against LPS-mediated lipid metabolism disorder in rats. Methods: Male Wistar rats were randomly divided and were administered tributyrin or vehicle orally 1 h before LPS injection and then sacrificed at 0, 1.5, 6, and 24 h after LPS. Liver tissue expressions of nuclear hormone receptors, enzymes associated with fatty acid metabolism, and histone acetylation were analyzed by real-time polymerase chain reaction or western blotting. Plasma lipids levels were measured. Results: Tributyrin enhanced expression of PPARs and histone H3 in the liver at basal levels. Tributyrin suppressed LPS-induced repression of PPARs fatty acid oxidation-associated enzymes: fatty acid transport protein and fatty acid binding protein, and fatty acid synthesis-associated enzyme: sterol regulatory element binding protein-1c. Tributyrin reduced the increase in plasma triglyceride, total cholesterol (TC), and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) levels at 24 h after LPS injection. Conclusions: Oral tributyrin administration prevented elevation of plasma triglyceride, TC, and LDL-C levels through improved fatty acid oxidation in endotoxemic rats.
Conclusion
In summary, our study showed that tributyrin reduces LPSinduced elevation of plasma TG, TC, and LDL-C levels through improved LPS-induced repression of fatty acid oxidation in the liver. Tributyrin administration might be a new therapeutic approach to recover from lipid metabolism disorder during acute inflammation such as sepsis.
如您需原文,请联系本文作者和出版方,或请垂询肠动力研究院。本网站发布的所有资料将尽最大可能注明出处、作者及日期,如无意中侵犯了您的知识产权,请来信及时告知,我们将立即予以删除。
All information released by the WeChat Official Account will do its best to indicate the source, author and date. If we inadvertently infringe on your intellectual property, please inform us in time and we will delete it immediately.






