原标题:敌草快处理下日粮添加三丁酸甘油酯可缓解仔猪的肠道炎症,同时增强线粒体功能和促进线粒体自噬
Dietary tributyrin attenuates intestinal inflammation, enhances mitochondrial function and induces mitophagy in piglets challenged with diquat
作者:Chunchun Wang†, Shuting Cao†, Qianhui Zhang†, Zhuojun Shen†, Jie Feng†, Qihua
Hong†, Jianjun Lu†, Fei Xie‡, Yan Peng‡ and Caihong Hu†*
† Animal Science College, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, 310058, P. R. China
‡ Shanghai Menon Animal Nutrition Technology Co. Ltd., Shanghai, 201807, P. R.
China
来源:J. Agric. Food Chem.,doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.8b06208•Publication Date (Web): 01 Jan 2019
翻译:肠动力研究院 梁琦
【摘要】该研究评估了以三丁酸甘油酯存在形式的丁酸对敌草快(一种除草剂)处理下猪的氧化应激,肠道炎症和线粒体功能的影响。24头断奶仔猪(35日龄,初始体重约为9.5kg)随机分成2×2因子处理组,每组6头。试验分组如下(1)S组:喂食基础日粮+10mg/kg生理盐水;(2)ST组:饲喂基础日粮+0.75g/kg三丁酸甘油酯+10mg/kg生理盐水;(3)D组:喂食基础日粮+10mg/kg敌草快;(4)DT组:饲喂基础日粮+0.75g/kg三丁酸甘油酯+10mg/kg敌草快;其中三丁酸甘油酯与基础日粮混合饲喂,试验为期2周,试验结束后将猪致死并采集相关样品进行分析。试验结果显示,DT组仔猪的平均日增重和平均日采食量显著增加(P <0.05)。此外,还发现DT组仔猪的总抗氧化能力和超氧化物歧化酶活性显著提高(P <0.05),丙二醛含量显著降低(P <0.05),铜和锌超氧化物歧化酶和含锰超氧化物歧化酶mRNA的表达水平显著提高(P <0.05)。在对仔猪肠道粘膜炎症因子的分析中发现,三丁酸甘油酯可通过降低肠道中TNF-α,IFN-γ和IL-6的mRNA丰度而缓解肠道炎症(P <0.05)。对仔猪肠道的通透性分析时发现,三丁酸甘油酯可显著降低血清二胺氧化酶活性和D-乳酸含量(P <0.05),增加跨肠上皮细胞电阻(P <0.05),降低葡聚糖的细胞旁通量(4 kDa),和防止敌草快引起的claudin-1,occludin和zo-1表达量的降低(P <0.05)。敌草快处理下仔猪日粮添加三丁酸甘油酯可缓解可缓解肠道上皮细胞线粒体功能紊乱,表现为活性氧降低、提高线粒体膜电位和ATP的含量(P <0.05)。此外,三丁酸甘油酯还增加了线粒体自噬蛋白(PTEN诱导的PINK1和Parkin)的表达量,以及肠道中轻链3-II与轻链3-I的比例(P <0.05)。研究结果表明,敌草快处理下日粮添加三丁酸甘油酯可缓解仔猪的氧化应激和肠道炎症,同时改善线粒体功能和促进线粒体自噬。
【关键词】三丁酸甘油酯;氧化应激;线粒体功能;线粒体自噬;肠道功能;猪
以下是实验中相关图表
表1:基础日粮的组成及成分

表2:实时定量PCR扩增的引物序列
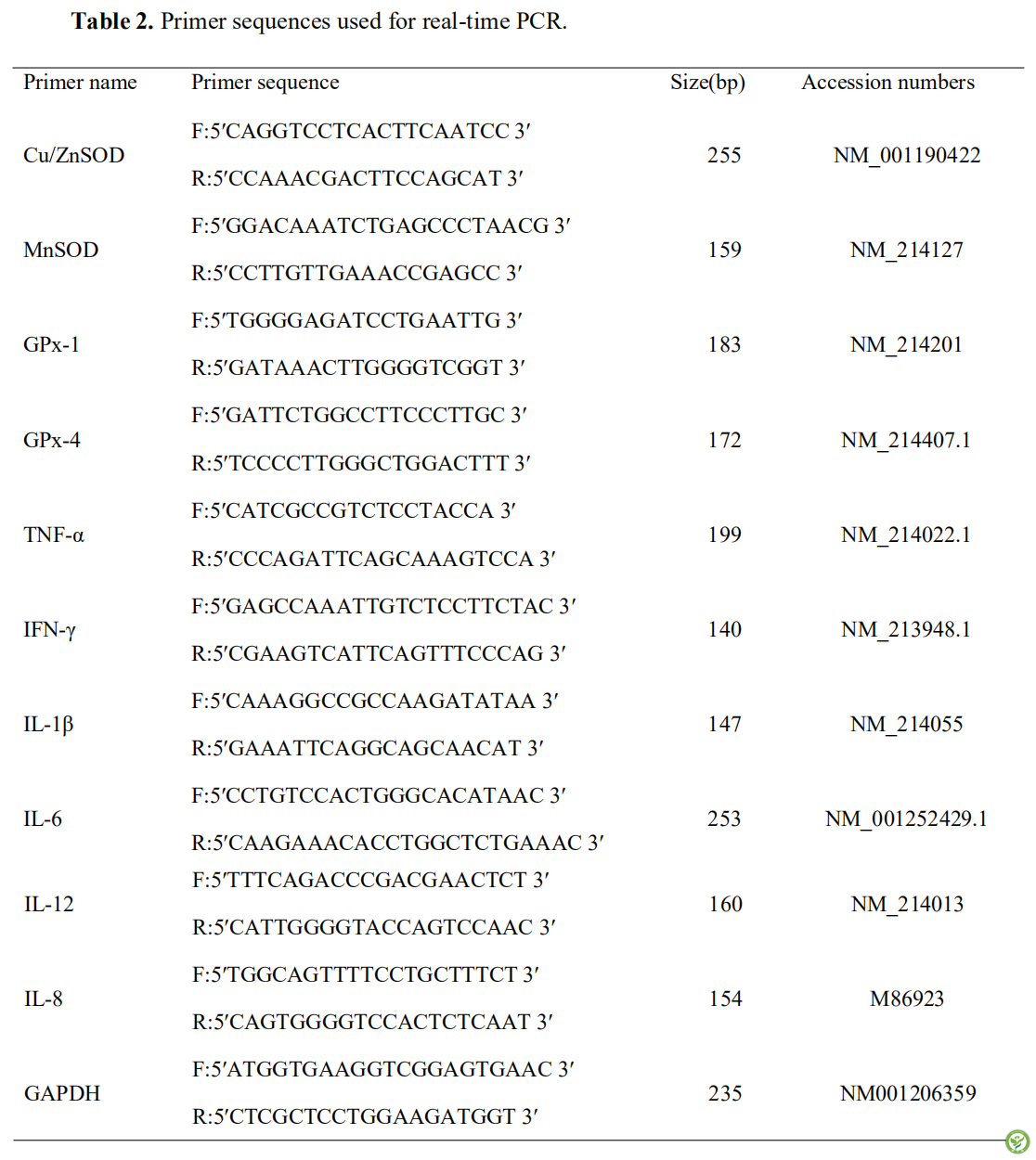
表3:日粮添加三丁酸甘油酯和敌草快处理对仔猪生产性能的影响
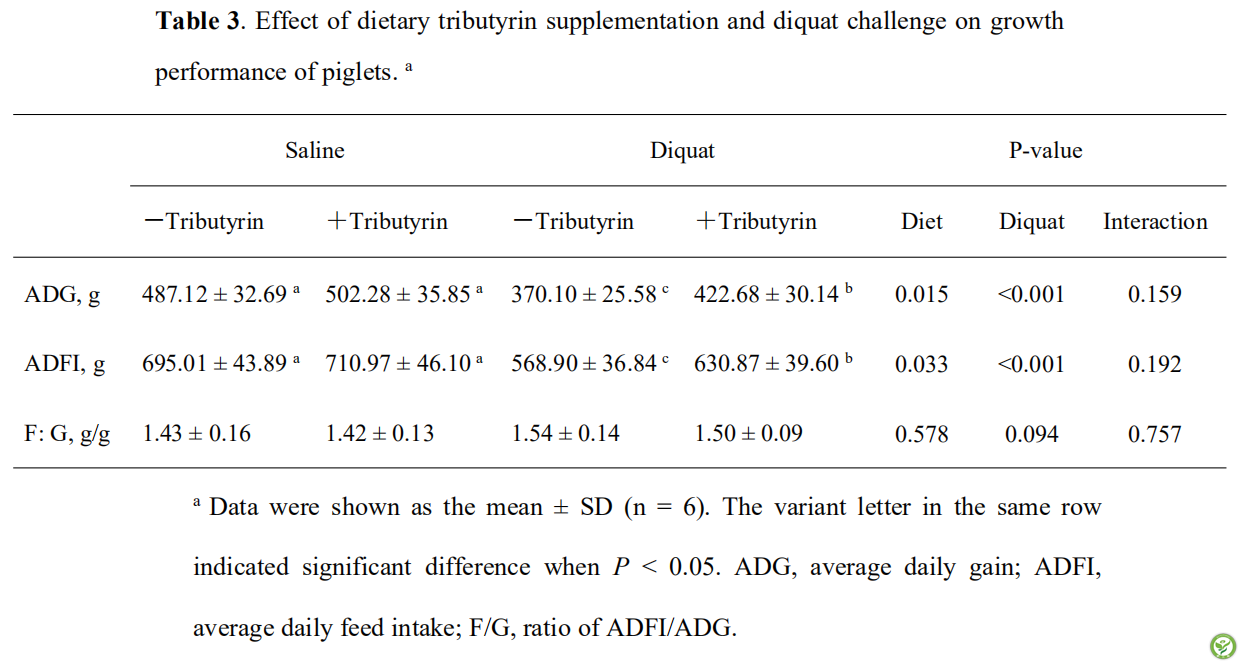
表4:日粮添加三丁酸甘油酯和敌草快处理对仔猪肠道粘膜中抗氧化酶活性和MDA含量的影响
表5:日粮添加三丁酸甘油酯和敌草快处理对仔猪肠道粘膜中抗氧化酶相关基因的mRNA表达量的影响

表6:日粮添加三丁酸甘油酯和敌草快处理对猪炎症细胞因子基因的mRNA表达量的影响
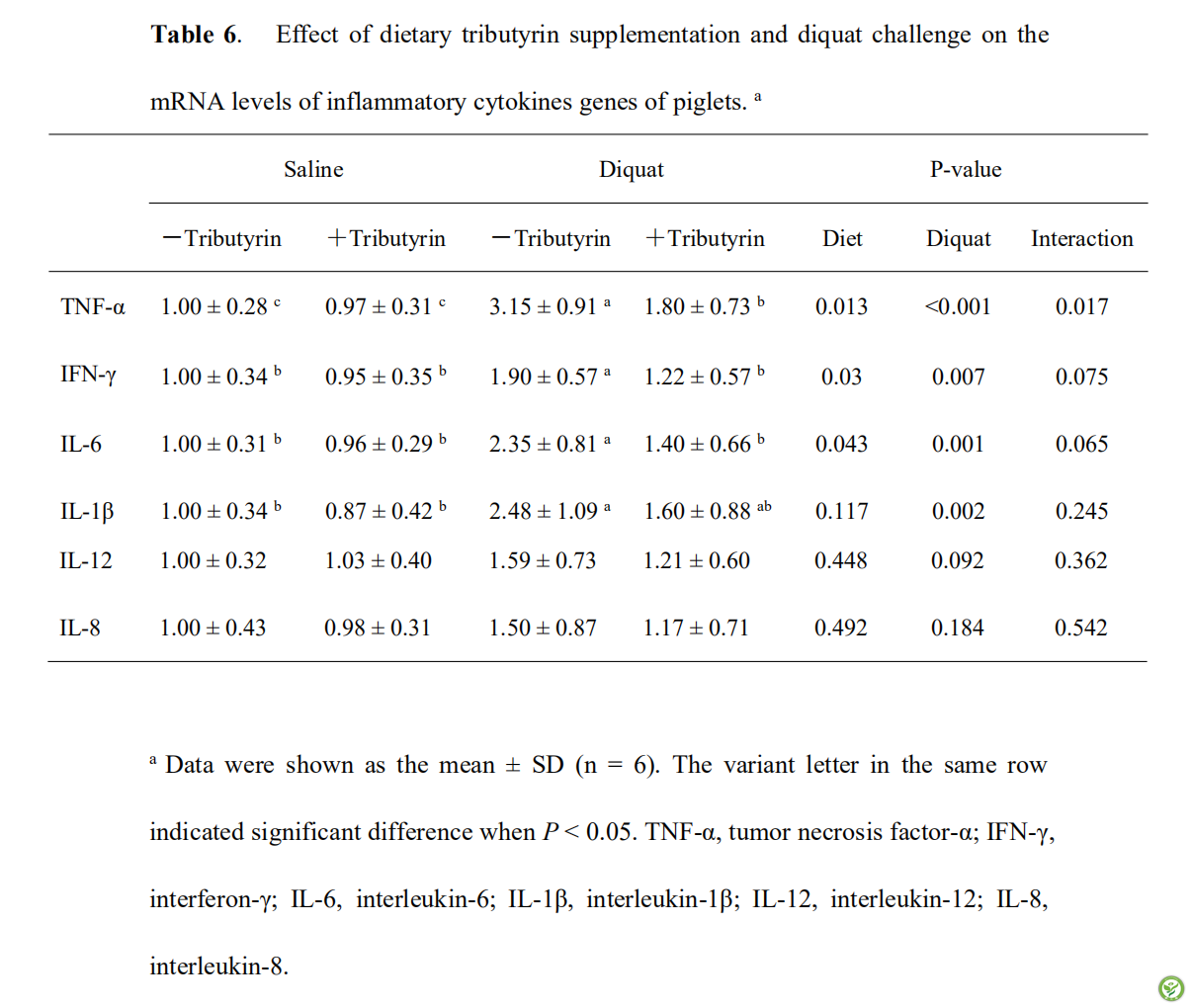
表7:日粮添加三丁酸甘油酯和敌草快处理对仔猪肠道通透性的影响
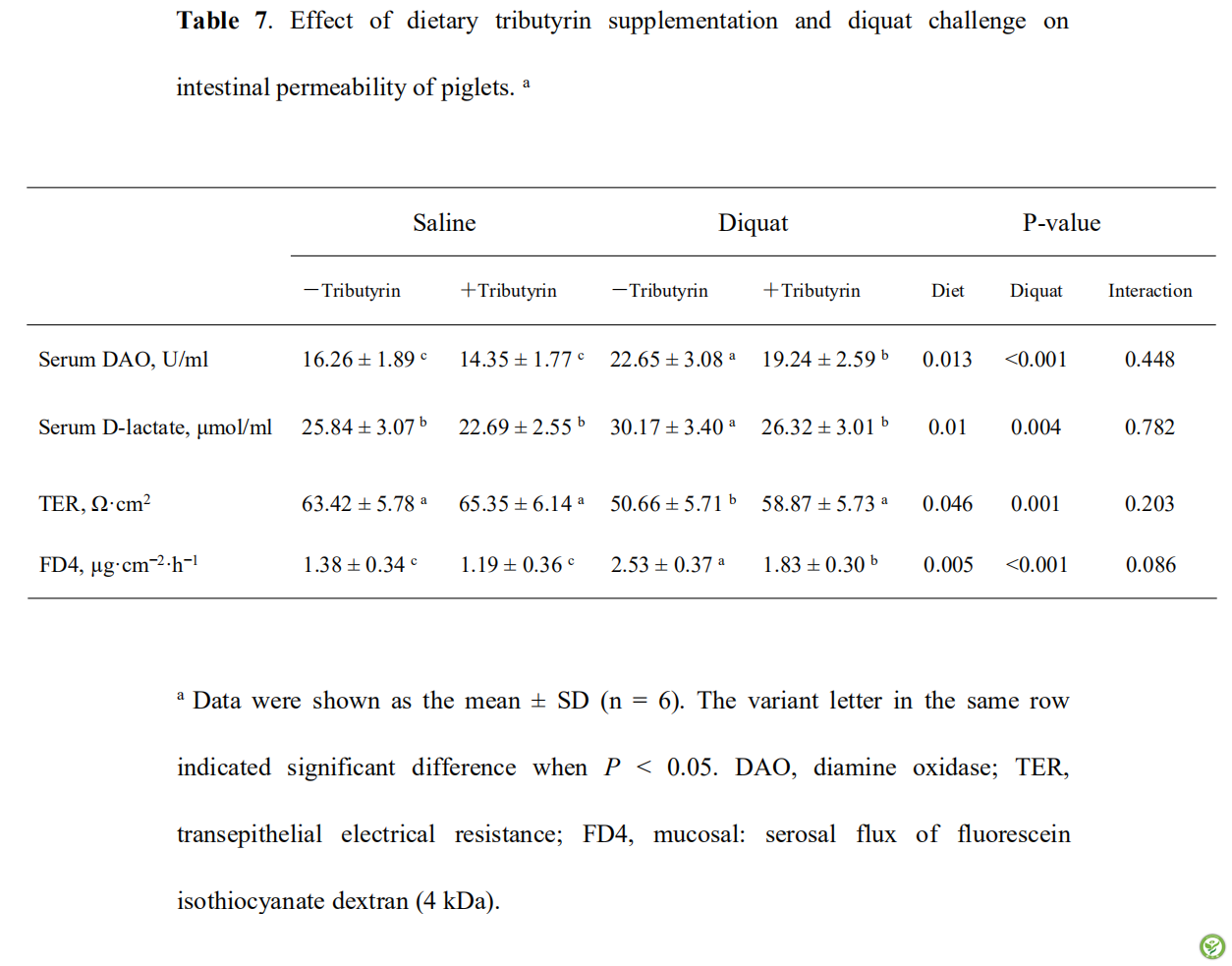
图1:
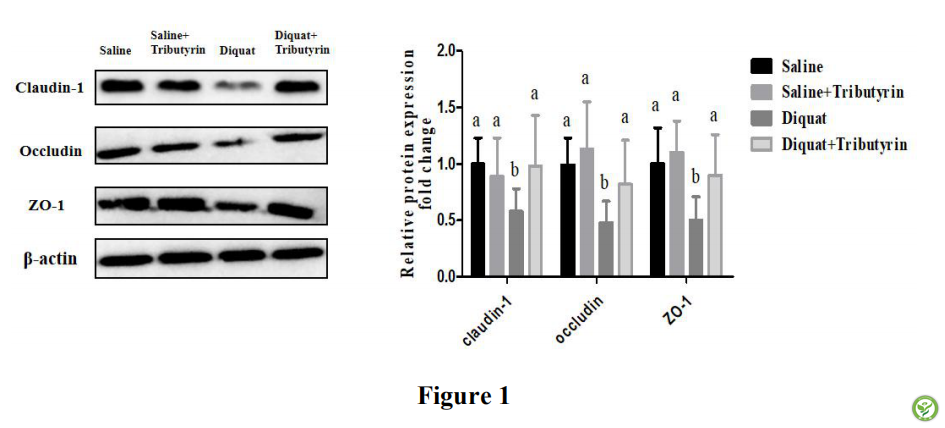
图2:
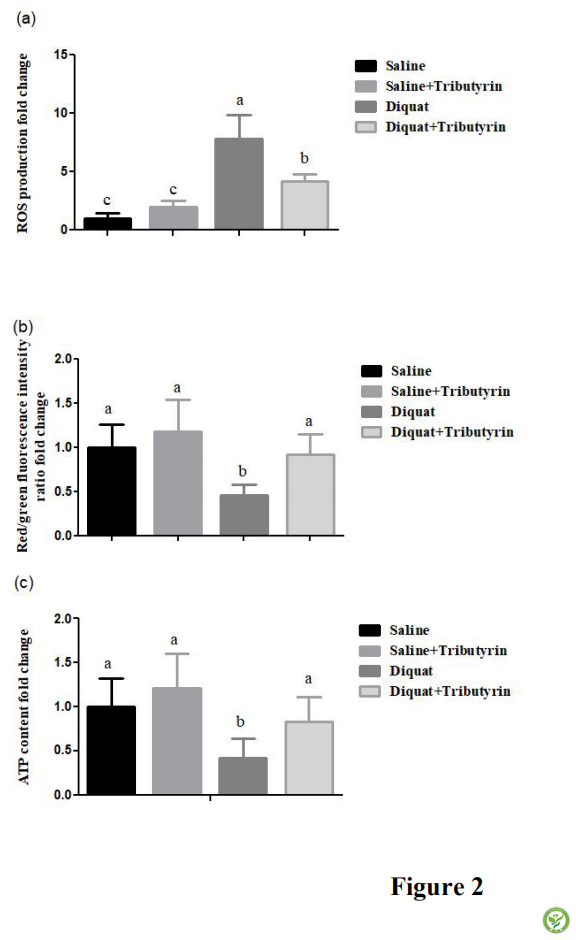
图3:
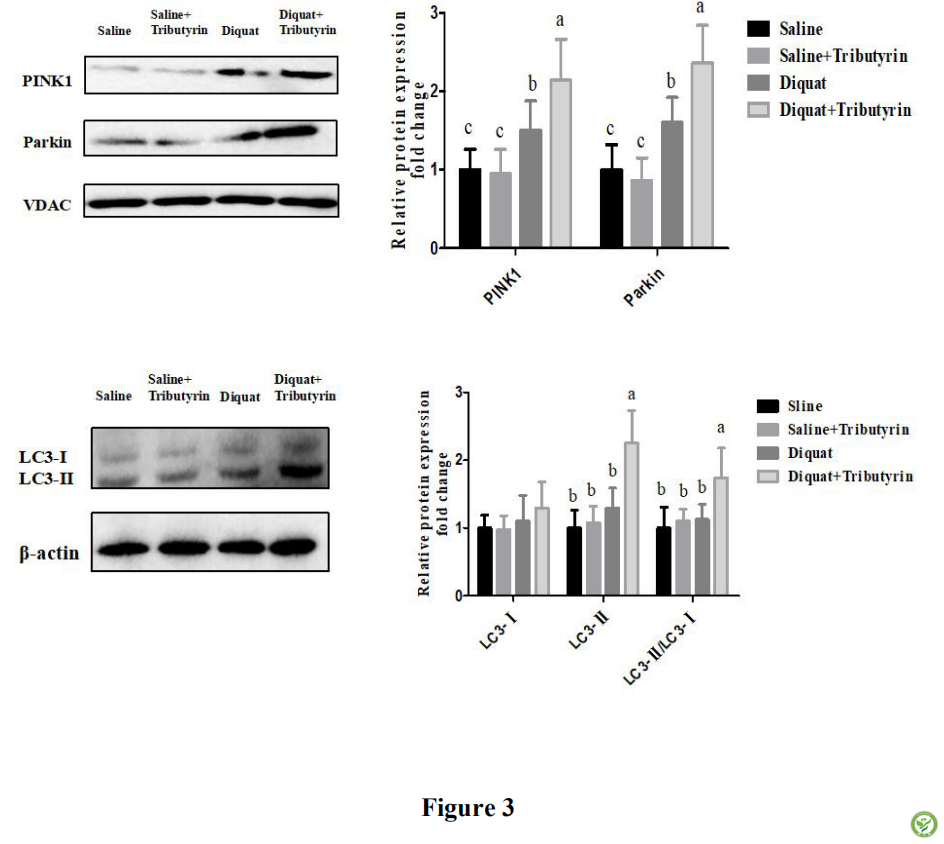
图4:
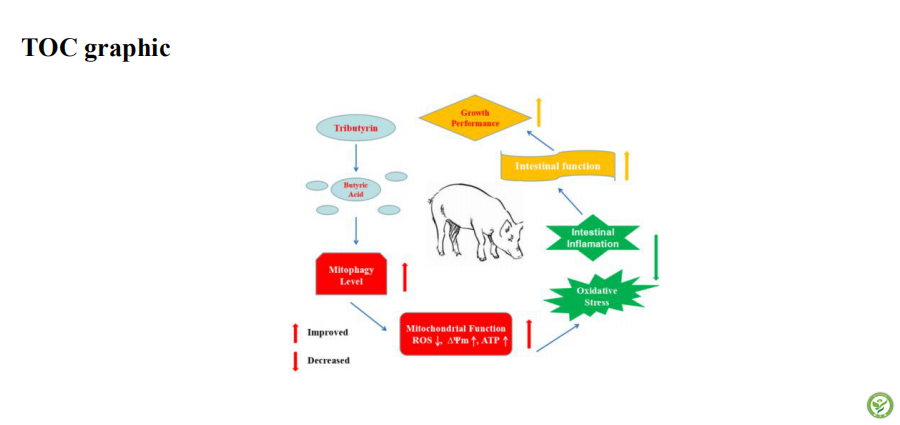
Implications
总之,本研究证实,敌草快处理下日粮添加三丁酸甘油酯可缓解猪的氧化应激和肠道炎症,同时改善线粒体功能和促进线粒体自噬。试验研究结果表明,三丁酸甘油酯通过促进线粒体自噬而缓解肠道氧化应激和炎症。这表明三丁酸甘油酯可以作为治疗动物和人中涉及氧化应激的肠道疾病的有效添加剂。
Abstract
The study evaluated the effects of butyric acid, in the form of tributyrin on the oxidative stress, inflammation and mitochondrial function in diquat-challenged pigs. Twenty-four weaned pigs were allocated to four treatments in a 2×2 factorial arrangement with the main effects tributyrin supplementation and diquat challenge The results showed that supplemental tributyrin increased (P <0.05) average daily gain and average daily feed intake of diquat-challenged pigs. Tributyrin elevated (P <0.05) the activities of total antioxidant capacity and superoxide dismutase, reduced (P < 0.05) malondialdehyde content, increased (P <0.05) mRNA levels of copper and zinc superoxide dismutase and manganese-containing superoxide dismutase of diquat-challenged pigs. Tributyrin relieved (P < 0.05) intestinal inflammation reflected by decreased mRNA abundances of tumor necrosis factor-α, interferon-γ, interleukin-6 in intestine. Tributyrin reduced (P <0.05) serum diamine oxidase activity and D-lactate content, increased (P <0.05) transepithelial electrical resistance, decreased paracellular flux of dextran (4 kDa), and prevented the diquat-induced decrease (P <0.05) in the expressions of claudin-1, occludin and zonula occludens-1.Tributyrin alleviated (P <0.05) diquat-induced mitochondrial dysfunction showed by lowered reactive oxygen species, increased mitochondrial membrane potential and adenosine triphosphate content. Furthermore, tributyrin increased (P <0.05) expressions of mitophagy proteins (PTEN induced putative kinase 1 and Parkin), and ratio of light chain 3-II to light chain 3-I in intestine. Collectively, tributyrin attenuated oxidative stress and intestinal inflammation, improved mitochondrial
Implications
In conclusion, the present study certificated that supplemental tributyrin attenuated the oxidative stress and intestinal inflammation, improved mitochondrial function and induced mitophagy in diquat-challenged pigs. Our results showed that tributyrin might induce mitophagy to relieve the intestinal oxidative stress and inflammation. This showed that tributyrin might serve as a effective additive to treat intestinal disorders involving oxidative stress in animal and human
如您需原文,请联系本文作者和出版方,或请垂询肠动力研究院。本网站发布的所有资料将尽最大可能注明出处、作者及日期,如无意中侵犯了您的知识产权,请来信及时告知,我们将立即予以删除。
All information released by the WeChat Official Account will do its best to indicate the source, author and date. If we inadvertently infringe on your intellectual property, please inform us in time and we will delete it immediately.










